- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Regelation is defined as the phenomenon in which the ice melts to the water below 0°C on the application of pressure and refreezes back to ice on the removal of pressure. Regelation demonstrates the idea of compressing the ice and turning it into water under pressure and when the pressure is removed, it solidifies again. A few of the examples of regelation are:
- Glacier acts as a source of a river due to regelation. The mass of the glacier exerts pressure on the lower surface lowering the melting point of the ice at its base. This results in the melting of ice and propels the glacier to slide over the liquid. Under appropriate conditions, liquid water flows from the base of the glacier to lower altitudes when the temperature of the air is above the freezing point of water.
- Preparation of an ice ball – The ice slab is shredded into pieces, and the shredded pieces are pressurized around the tip of a stick to prepare the ice ball. If two small pieces of ice are taken and pressed against each other, they stick to each other.
Regelation of Ice
The regelation of ice can be better understood by performing an experiment on an ice slab using a metallic wire. The procedure of the experiment is given below.
Procedure:
- For the experiment, take a slab of wire and a metallic wire with 5 kg of blocks attached to it on either side.
- Put the wire over the glass slab, as shown in the diagram.
What happens next?
It observed that the wire gradually penetrates and passes through the ice slab. This happens due to the fact that the ice melts at a lower temperature due to the increase in pressure just below the wire. When the wire has crossed, water above the wire solidifies. Hence, the wire passes through the slab without splitting it. This phenomenon of refreezing is known as regelation.
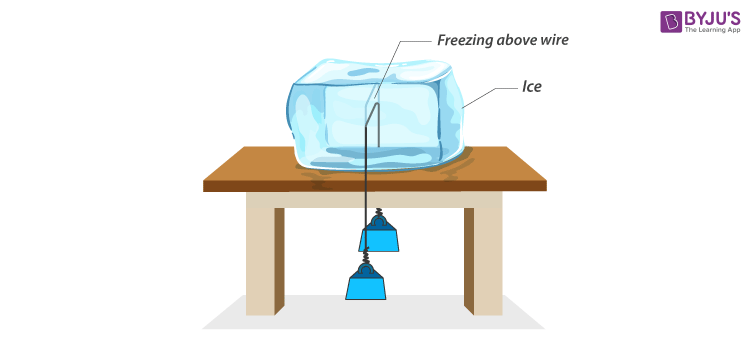
The wire gradually penetrates through the ice
Here, the melting point of the ice becomes lower than 0°C due to the applied pressure. This implies that at 0°C ice is converted into water and as soon as the pressure is removed the melting point is restored back to 0°C and the water is converted back to ice again.It is due to regelation that skating is possible on snow due to the formation of water. Water is formed due to the increase of pressure and it serves as a lubricant.
It happens due to Charles law, Pressure is directly proportional to temperature.
When you bring a water a container or something in the space where is absolute volume, The kinetic energy of water molecules get exhausted in boiling the water, results in freezing of water. This is because when we reduce a pressure to much, the boiling point of water also reduces.
Image credit: Byjus
Comments
Post a Comment
THANKS A LOT🥰😊